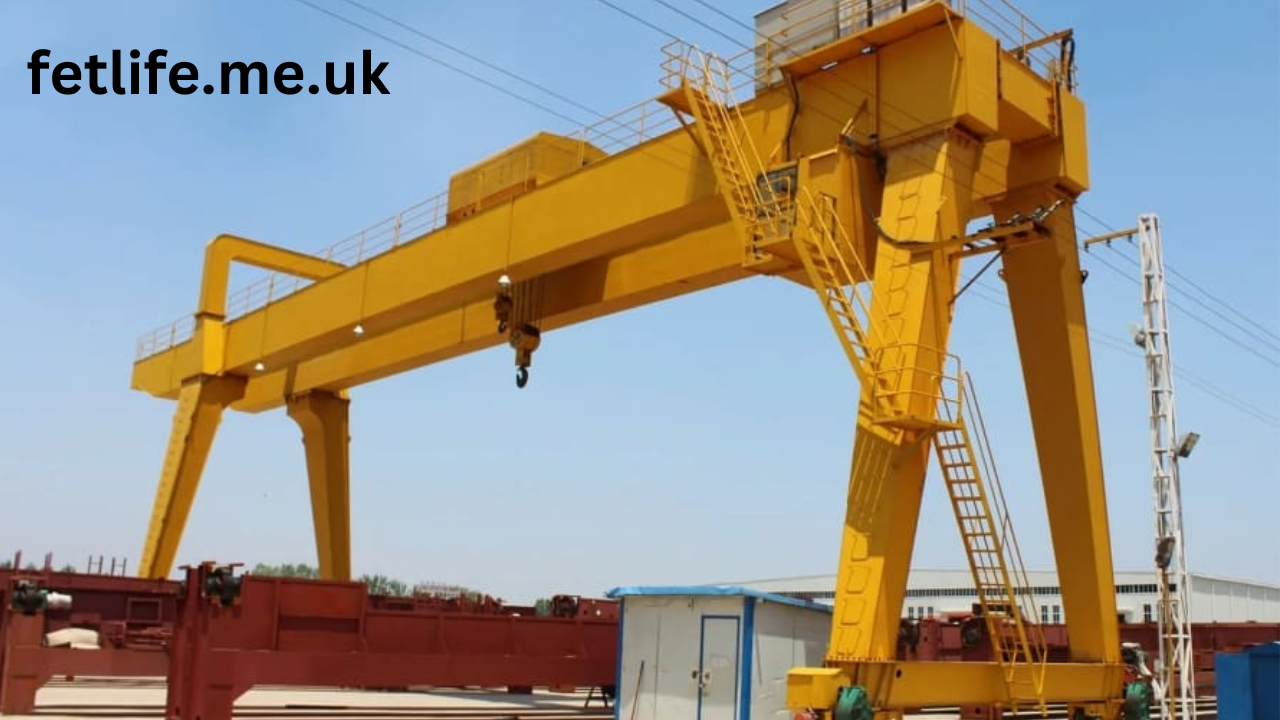
The Second World War stands as one of the most transformative periods in modern history, shaping global political, economic, and technological landscapes. Among the myriad innovations necessitated by wartime demands, ww2 german railway gantry crane emerged as a vital component in the logistics network of the Third Reich. These cranes embodied the marriage of precision engineering and practical utility, serving as pivotal tools for the efficient transportation of military equipment, raw materials, and other wartime necessities. This article explores the design, usage, and historical significance of German railway gantry cranes during World War II, illuminating their role in the broader context of wartime engineering and logistics.
The Role of Logistics ww2 german railway gantry crane
Logistics is often cited as the backbone of any military campaign, and this was particularly true during World War II. With vast armies, extensive supply lines, and a relentless demand for materials, the German military relied heavily on an efficient transportation network. Railways formed the core of this network, enabling the movement of troops, tanks, ammunition, and supplies across the expansive territories under Nazi control.
The efficiency of this railway network was heavily dependent on the ability to load and unload cargo swiftly and safely. Ww2 german railway gantry cranes were designed to address this challenge, providing a reliable means of handling heavy loads that were otherwise impossible to move manually or with simpler equipment.
Design and Engineering of German Railway Gantry Cranes
German railway gantry cranes were characterized by their robust construction, precision engineering, and adaptability. These cranes were typically mounted on rails, allowing them to traverse freight yards or industrial sites with ease. Their design featured a horizontal gantry structure supported by vertical columns, with a movable hoist mechanism capable of lifting and transporting heavy loads.
Key Features of WW2 German Gantry Cranes:
- Capacity for Heavy Loads:
These cranes were engineered to handle loads ranging from several tons to over 100 tons, making them suitable for lifting tanks, artillery pieces, and industrial machinery. - Mobility:
Mounted on railway tracks, gantry cranes could move laterally along the rails, covering large areas and accessing different sections of freight yards or depots. This mobility was crucial for maximizing operational efficiency. - Precision and Reliability:
German engineering was renowned for its precision, and gantry cranes were no exception. They featured advanced mechanisms for the time, including electric or hydraulic hoists that ensured smooth and accurate movement of heavy loads. - Durability:
Constructed from high-quality steel, these cranes were built to withstand the rigors of wartime operations, including exposure to harsh weather conditions and potential bombings. - Modularity:
Many gantry cranes were modular in design, allowing for quick assembly and disassembly. This feature was particularly useful when relocating cranes to new operational areas.
Applications of ww2 german railway gantry crane
German railway gantry cranes played a crucial role across various sectors during World War II. Their versatility made them indispensable in numerous contexts:
1. Military Logistics
The primary use of these cranes was in military logistics. They were deployed at railway depots and ports to load and unload heavy military equipment, such as tanks, artillery, and armored vehicles. As the German military expanded its operations into Eastern Europe and beyond, the demand for rapid and efficient transportation systems increased, necessitating the widespread use of gantry cranes.
2. Industrial Production and Supply
Germany’s war machine relied heavily on its industrial base, which produced everything from weapons to vehicles. Gantry cranes were essential in factories and industrial yards for moving raw materials, assembling machinery, and loading finished products onto railway cars for distribution.
3. Construction and Infrastructure
The construction of military fortifications, airfields, and other infrastructure required significant material handling capabilities. Ww2 german railway gantry cranes were often used to transport construction materials, including steel beams, concrete components, and other heavy items.
4. Shipbuilding and Repair
In naval yards, gantry cranes were indispensable for constructing and repairing ships. They were used to lift ship components and equipment, facilitating the rapid production of naval vessels needed for the war effort.
Notable Examples of German Gantry Cranes
While many gantry cranes used during World War II were utilitarian in nature and lacked distinctive individual identities, a few notable examples stood out due to their size, capacity, or unique engineering features.
Previous article; Common Problems and Solutions for zbook14 g2 key replace
The Krupp Gantry Cranes
Krupp, one of Germany’s leading industrial firms, was a key manufacturer of heavy machinery during the war. The company produced gantry cranes specifically designed for handling oversized loads, such as naval guns and tank components. These cranes were known for their immense lifting capacity and robust construction.
Port Cranes in Hamburg and Bremen
The port cities of Hamburg and Bremen were vital hubs for Germany’s wartime logistics. Massive gantry cranes in these ports facilitated the loading and unloading of military cargo, including U-boat components and other naval equipment. Their strategic importance made them prime targets for Allied bombers.
Challenges and Limitations ww2 german railway gantry crane
Despite their utility, German railway gantry cranes faced several challenges during the war.
- Vulnerability to Bombing:
As fixed or semi-fixed installations, gantry cranes were susceptible to air raids. Allied bombers targeted railway yards and industrial facilities, often destroying cranes and disrupting logistics operations. - Resource Constraints:
The scarcity of raw materials and skilled labor in the latter stages of the war affected the production and maintenance of gantry cranes. This limitation hampered Germany’s ability to sustain its logistics network effectively. - Operational Limitations in Remote Areas:
While gantry cranes were highly effective in established depots and industrial zones, their utility was limited in remote or underdeveloped areas where railway infrastructure was less developed.
Legacy of German Railway Gantry Cranes
The end of World War II marked the decline of Germany’s wartime logistics infrastructure, including its gantry cranes. However, their impact on engineering and logistics practices was far-reaching. Many of the design principles and technologies pioneered in these cranes influenced post-war industrial and logistical developments worldwide.
In the decades following the war, gantry cranes continued to evolve, becoming larger, more efficient, and more versatile. Modern gantry cranes, used in ports and industrial facilities around the world, owe much of their design heritage to the innovations of the wartime era.
Conclusion
The ww2 german railway gantry crane represent a fascinating intersection of engineering ingenuity and wartime necessity. As critical components of the Third Reich’s logistics network, these cranes facilitated the efficient transportation of military equipment and materials, playing a vital role in Germany’s war effort.
While the war ultimately ended in defeat for Germany, the technological achievements embodied in these cranes left a lasting legacy. They serve as a testament to the importance of logistics and engineering in shaping the outcomes of history’s most significant conflicts.
Today, the remnants of these cranes, whether preserved in museums or rusting in forgotten railway yards, stand as silent witnesses to an era of unprecedented industrial and military activity—a poignant reminder of the enduring impact of wartime innovation.